Cryptography is the study of how to secure data and transfer it without readable format with help of various Encryption algorithms and decryption algorithms, such as Symmetric Key cryptography, Asymmetric key cryptography, Hash Algorithms and cryptography objective which are as 1) Confidentiality 2) Integrity 3) Non repudiation 4) Authentication etc. and its methods . We will see in detail about all cryptography functionality in this article.
In general cryptography is about constructing and analyzing protocols that prevent third parties or the public reading private messages and transactions. We will see all parameter of modern cryptography like Encryption algorithms ,decryption algorithms ,cyphertext, public key ,private key and mainly Hash algorithms in details.
History of Cryptography
“”Cryptography” this word is derived from the Greek “kryptos” word which means hidden. The prefix “Crypt” means hidden or vault and the suffix ”graphy” means writing. We can consider cryptography duration or era in three types by the time and technology. These are as follows.
Classic Cryptography
In the ancient world and civilization ,before the modern era of cryptography, cryptography focused on message confidently. The main classical cipher types are transposition ciphers where Julius Cipher used the first known cipher also known as Caesar Cipher.
Modern Cryptography
Modern cryptography is a method of developing techniques and protocols to prevent a third party from accessing data. From now we are looking only at modern cryptography and its function and real time application.
Objective of the modern cryptography
- Confidentiality
The information can not be understood till the desired location or receiver is not fulfilled.
- Integrity
Information can not be altered or edited in between processes.
- Non-repudiation
Intentions of data transmission can not deny in between process by sender
- Authentication
The sender and receiver must confirm each other’s identity to complete data transmission.
Types of Cryptography
Symmetric-key Cryptography
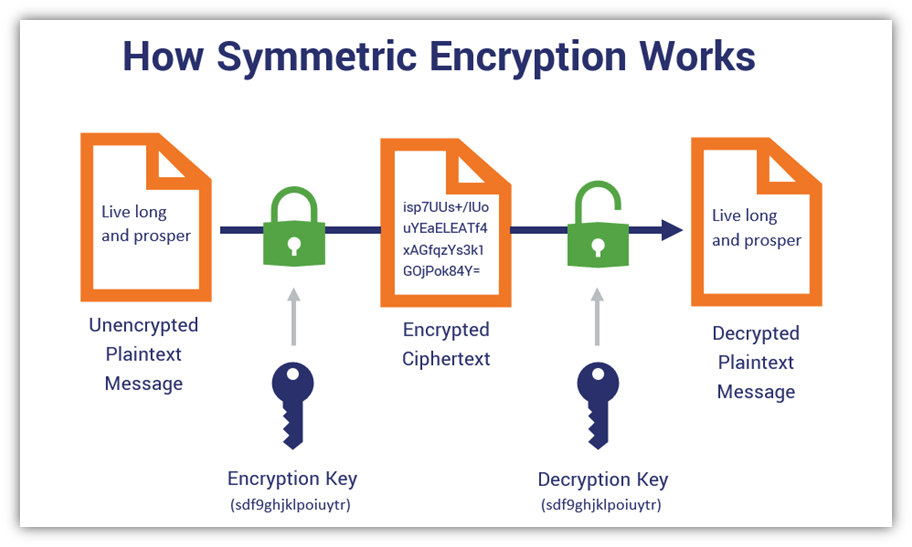
Symmetric-key cryptography also known as Single-key encryption algorithms. This algorithms create blocks with fixed length of bits which is known as block cipher.
In Symmetric-key cryptography the sender uses one key to encrypt plain text into the cipher and send it to the receiver, the receiver applies the same key to decrypt the message and recover the original text.
Symmetric-key cryptography: both the sender and receiver share the same single key to process data. Example of Symmetric-key cryptography as follows.
AES:- Advanced encryption standard
Asymmetric-key or Public-Key encryption
Asymmetric-key algorithms use two different keys to complete transaction security. These types are as follows.
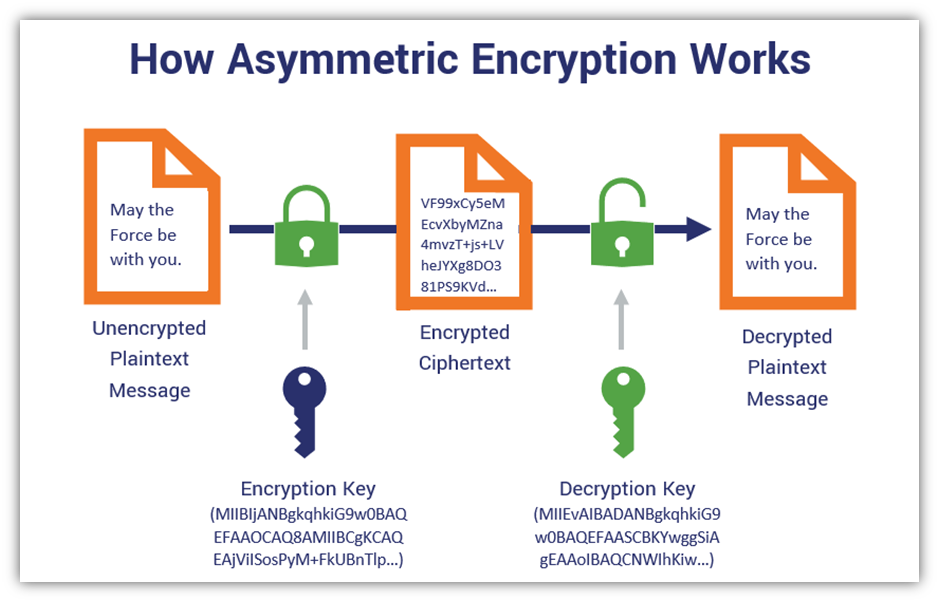
*Public-Key
Public-key related to sender for encrypting plain text into the cipher. Public-key may be distributed but without private key one can not decrypt message or data. Public key used for only encrypting data.
*Private-Key
Private-key used by the receiver to decrypt the cipher text into original data or plain text, it means Private-key used for only decrypting data.
Following are some examples of Asymmetric encryption algorithms.
- RSA-Algorithms
- DSA-Digital signature Algorithms.
Hash Algorithms
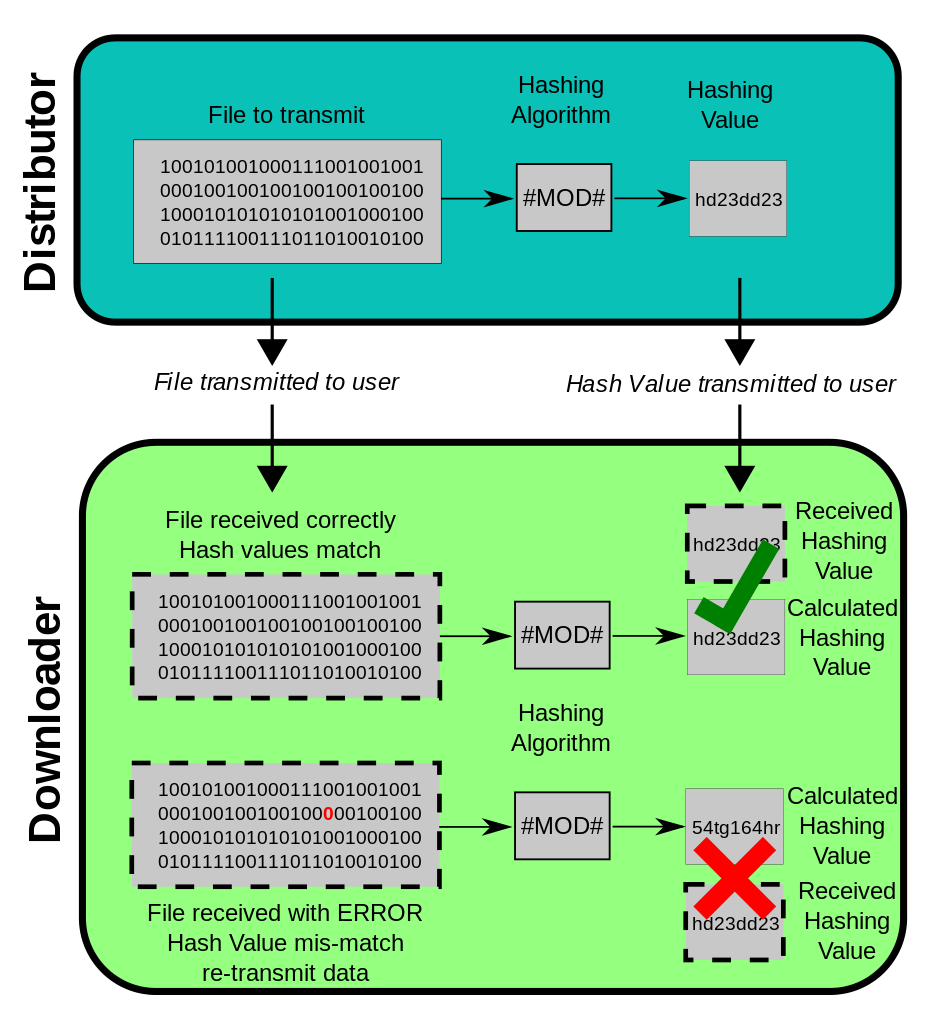
Instead of key,Hash algorithms use fixed-length hash value,as par input data to secure data.Hash algorithms are one-way functions,which means message or data is not possible to reverse in original format.
Hash algorithms have some unique properties. These are as follows.
1) Determinish
Meaning the same message always results in the same hash.
2) Collision resistance
It should be hard to find two different passwords that hash to the same cipher.
3) Diffusion or Avalanche effect
By making a change in one bit of original text or data ,result in change to half bit of its hash.
4) Non-Predictable
The hash value should not be predictable from the password.
5) Non-Reversibility
It is impossible to reserve a transaction and get original data or text back in hash algorithms.
Concussion
Hash algorithms are widely used for secure blockchain technology. There are many algorithms and applications developed on Hash Algorithm cryptography. One of the most applications developed on this algorithms is Blockchain which the most advanced technology used for secure transaction now days.
MD5,SHA 01,2,256 These are some example of algorithms of Hash cryptography.
Bitcoin is the best example of real time Blockchain application which developed on Hash cryptography and there so many cryptocurrency developed on Hash algorithms cryptography.
This way cryptography is the most important technology in now and future for secure our data and transaction and much more.


